IVF

Fertility treatments - IVF
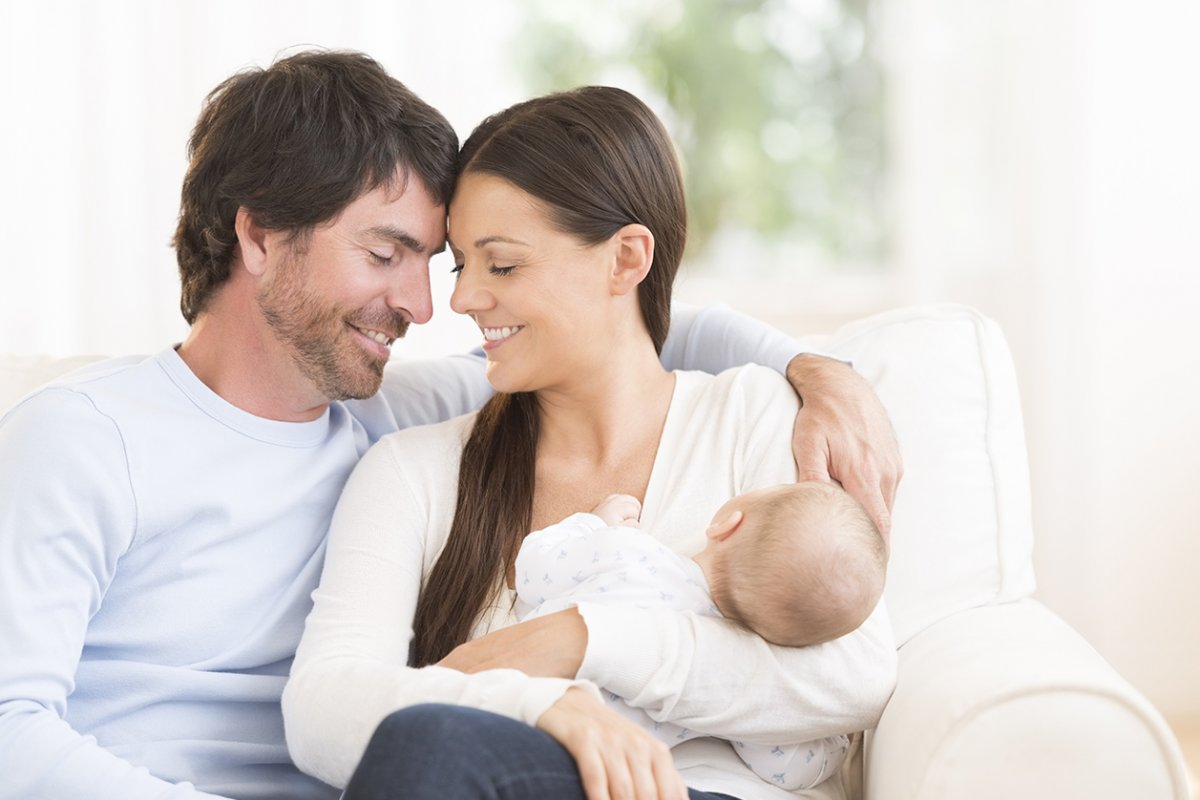
What is IVF?
In Vitro literally means ‘in glass'. So In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) actually means ‘fertilisation in glass', or freely translated: ‘fertilisation outside the body.' IVF is used when natural fertilisation turns out not to be possible. One or more eggs are brought together with sperm outside the body to achieve fertilisation. If this is successful, the fertilised eggs (embryos) are placed back in the womb and a pregnancy may result.
IVF may be used to overcome female or male infertility problems and may be an option if you or your partner has:
- Fallopian tube damage or blockage
- Ovulation disorders
- Premature ovarian failure
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Previous tubal sterilization or removal
- Impaired sperm production or function
- Unexplained infertility
- A genetic disorder
- Fertility preservation for cancer or other health conditions
Belgium is known for having artificial insemination centers specialized in IVF.
Chances of success?
Many people are unaware of the fact that the chance of pregnancy for a perfectly fertile couple within a normal cycle is only 20%. Over time, however, these people do conceive relatively quickly, because there is a new chance of doing so every month.
IVF can offer a solution to couples who do remain childless. This technique is also used more and more often. Because more than one embryo is put back into the womb in most cases, the chance of pregnancy after a first round of IVF treatment is even slightly higher than with ordinary, natural fertilisation. Of course this does not mean that every couple is certain to conceive immediately. If a first attempt is unsuccessful, the treatment can be repeated for several successive cycles. If more suitable embryos are obtained during IVF fertilisation than can be placed in the womb, these can also be stored (cryopreservation). This increases the chances of a successful pregnancy even further without needing repeated stimulations and/or oocyte retrievals.
However, we should certainly add here that further complications can occur in the crucial first weeks of a pregnancy. This is why our patients receive intensive, expert monitoring during that period, because this is a difficult time for them emotionally with feelings of fear as well as joy.
The effect of age is obvious:
- At a young age you easily become pregnant: the first treatment cycles result in a high chance of pregnancy
- At a later age every treatment cycle results in a comparable but lower cumulative chance of pregnancy
- it is more difficult to get pregnant (lower chance of implantation)
- it is more difficult to stay pregnant (higher risk of miscarriage)
- For the group of women in the 40 to 42 age category, ten out of a hundred who start the first treatment cycle will deliver a baby. After the fourth treatment cycle, 38 women out of a hundred will have delivered a baby
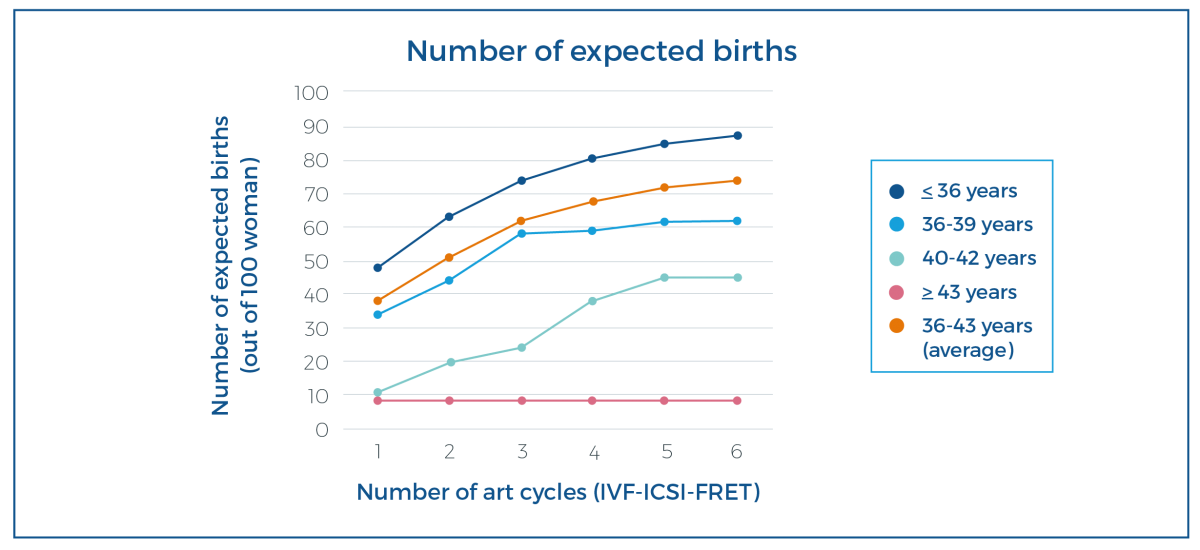
On the vertical line you can see how many women (out of a hundred) in which age category will have delivered a baby after IVF-ICSI-treatment with possible transfer of fresh and frozen-thawed embryos.
The horizontal line shows the number of treatment cycles.
Legal restriction
Belgian law lays down an absolute age limit for fertility treatment:
- Egg retrieval is possible up to your 45th birthday (to the day before you turn 45)
- For an embryo transfer the age limit is 47 (the day before you turn 48) - in other words, you are required to have had your egg retrieval before your 45th birthday to qualify for an embryo transfer later. (possibly with thawed embryos)
- As soon as you turn 48, you can no longer be treated in Belgium.
IVF procedure
What happens during IVF treatment?
- Consultation
- Stimulation (medication)
- Oocyte retrieval (removal of the mature egg cells)
- Fertilisation (conception itself)
- Transfer (placing an embryo or embryos back in the womb)
- Result
More information about the IVF procedure
Special treatments
Which special forms of IVF exist and which ones apply when?
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- Microscopic Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA)
- Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE)
- Assisted Hatching
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) or Screening (PGS)
More information about all special treatments
How are sperm, eggs and embryos stored?
Cryopreservation and Vitrification